
16:13 - 16:16
S28-3
(PP)
★
PEDIATRIC LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY: OUTCOME ANALYSIS OF INFANTS
VERSUS OLDER CHILDREN
Chandrasekharam VVS
Ranbow Children's Hospitals, Pediatric Urology, Pediatric Surgery & MAS, Hyderabad, INDIA
PURPOSE
Laparoscopic pyeloplasty(LP) is less popular and considered less successful in infants compared to older children. The
aim of this paper is to compare the results of LP in infants(group 1) with children over 1 year of age(group 2)
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The data of all children undergoing LP by a single surgeon between March 2009 and August 2014 was retrospectively
analysed for patient details and follow-up. Both groups had Ultrasound and Diuretic renogram pre-operatively and for
followup. A significant reduction of hydronephrosis (measured by anteroposterior diameter of the renal pelvis) on follow-
up and/or improvement of drainage on diuretic renogram was considered to indicate successful pyeloplasty. The various
parameters were compared between the two groups. Statistical analysis was done using software; student t test and
chi-square test were applied.
RESULTS
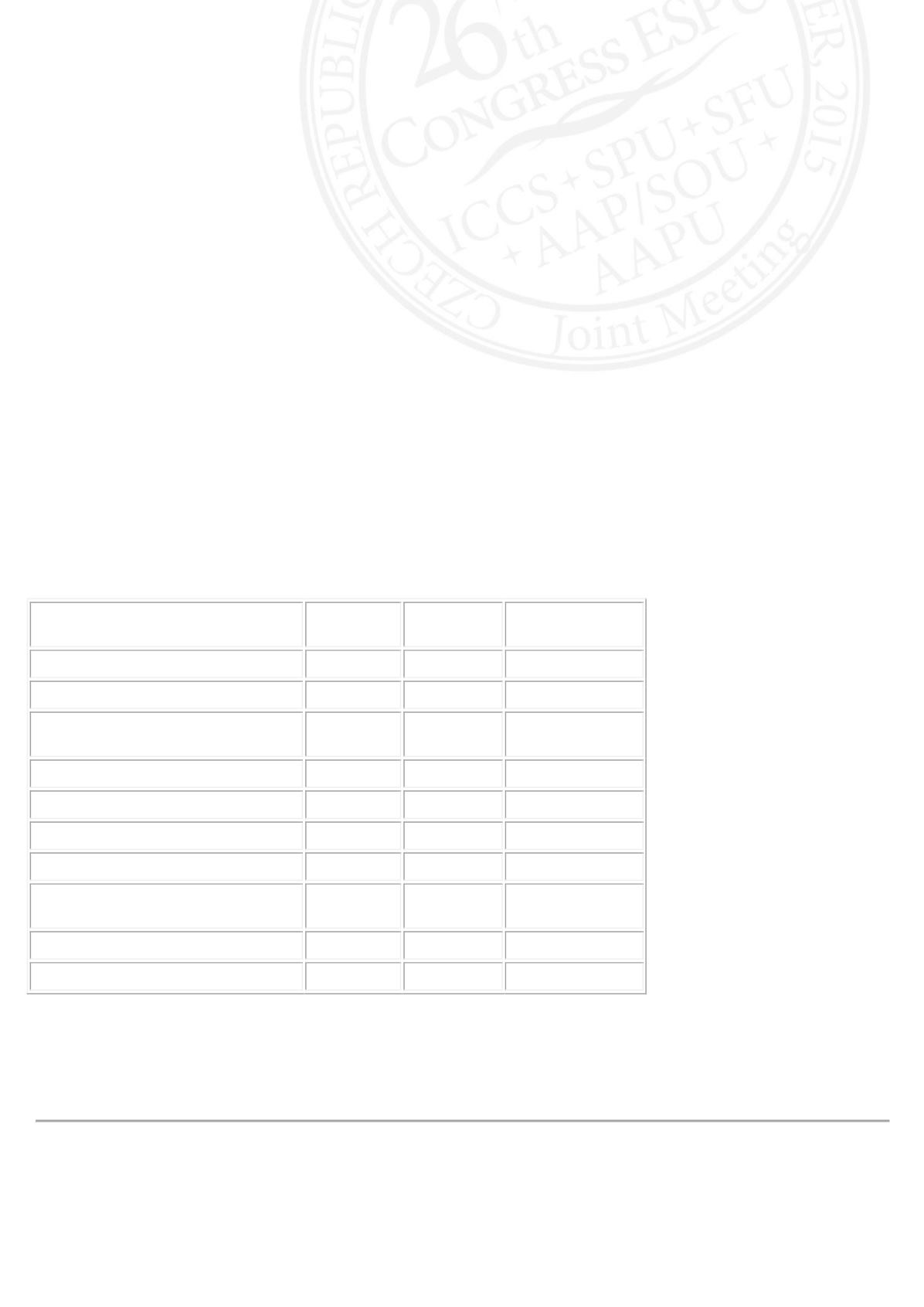
The various parameters of both the groups are summarized in table 1. There was no difference in the success of LP or
complications in both groups. Significant reduction in hydronephrosis and improvement in mean differential function on
follow-up was noted in both groups. The operating time was longer in group 2 but the difference was not statistically
significant; group 2 had more children with extrinsic obstruction. Group 1 had more children requiring bilateral LP, and
significantly more kidneys demonstrating functional improvement (>10%) after surgery.
Parameter
group 1
group 2
p value (group 1
vs 2)
no of patients
167
94
mean age mo
4.0+/-3.03 54.3+/-37.2
mean wt kg
5.62+/-
1.48
16.45+/-
9.38
bilateral operation
7 (4%)
1 (1%)
p= 0.04
extrinsic obstruction
7 (4%)
12 (13%)
p< 0.001
OT mean min
104
121
complications
17(10%)
7(7.5%)
kidneys with post-op function
increase > 10%
51/98
(52%)
17/47
(36%)
p= 0.01
success
99%
100%
median follow-up(mo)
18
12
CONCLUSIONS
LP can be safely and successfully done in infants, with success comparable to older children, with greater chance of
functional improvement of the affected kidney.












