
16:16 - 16:22
ICCS S2-2
(LO)
SOLIFENACIN IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH OVERACTIVE BLADDER:
RESULTS OF A PHASE 3 CLINICAL TRIAL
Donald NEWGREEN
1
, Brigitte BOSMAN
1
, Will SAWYER
2
, Adriana HOLLESTEIN-HAVELAAR
3
, Robin BESUYEN
3
, Ellen
DAHLER
4
, Stéphane BOLDUC
5
and Soeren RITTIG
6
1) Astellas Pharma Europe BV, Global Medical Science - Urology / Nephrology, Leiden, NETHERLANDS - 2) Astellas
Pharma Europe BV, Global Development Operations Biostatistics II, Leiden, NETHERLANDS - 3) Astellas Pharma Europe
BV, Global Development Operations, Clinical Science, Leiden, NETHERLANDS - 4) Astellas Pharma BV, Global
Development Operations Clinical Study Management, Leiden, NETHERLANDS - 5) CHU de Québec, Division of Urology,
Québec, CANADA - 6) Aarhus University Hospital, Department of Pediatrics, Aarhus N, DENMARK
PURPOSE
To evaluate efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of solifenacin succinate oral suspension in children (5–11 yrs) and
adolescents (12–17 yrs) with overactive bladder.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Following 2-week, single-blind placebo run-in, subjects with >4 daytime incontinence episodes in a 7-day diary were
randomized to 12 weeks’ once-daily solifenacin/placebo+standard urotherapy. Solifenacin starting doses, based on
subject’s weight at screening, aimed to deliver steady-state plasma drug exposure equivalent to the 5 mg tablet dose in
adults (PED5). Titration was in steps of 3-weeks duration to attain optimal individual doses at Week 9 (final doses
equivalent to PED2.5 to PED10). Primary efficacy variable: change from baseline to end of treatment in Mean Volume
Voided (MVV)/micturition. Key secondary endpoints: mean number of incontinence episodes and micturitions/24 hrs.
Efficacy was assessed using a 7-day diary.
RESULTS
148 children and 41 adolescents were randomized. Children on solifenacin had a greater increase in MVV/micturition vs
those on placebo (Table; P=0.046). There were no statistically significant differences between solifenacin and placebo in
incontinence or micturition frequency in children, or for primary or key secondary endpoints in adolescents (not
powered). Exploratory analyses demonstrated statistically significant reductions in micturition frequency vs placebo
when adjusted for change in fluid intake. Most common drug-related TEAEs are shown (Table). Solifenacin did not
increase PVR volume. Increase from baseline in mean corrected QT interval with solifenacin was 4.2 ms; below the
threshold of clinical concern (5 ms).
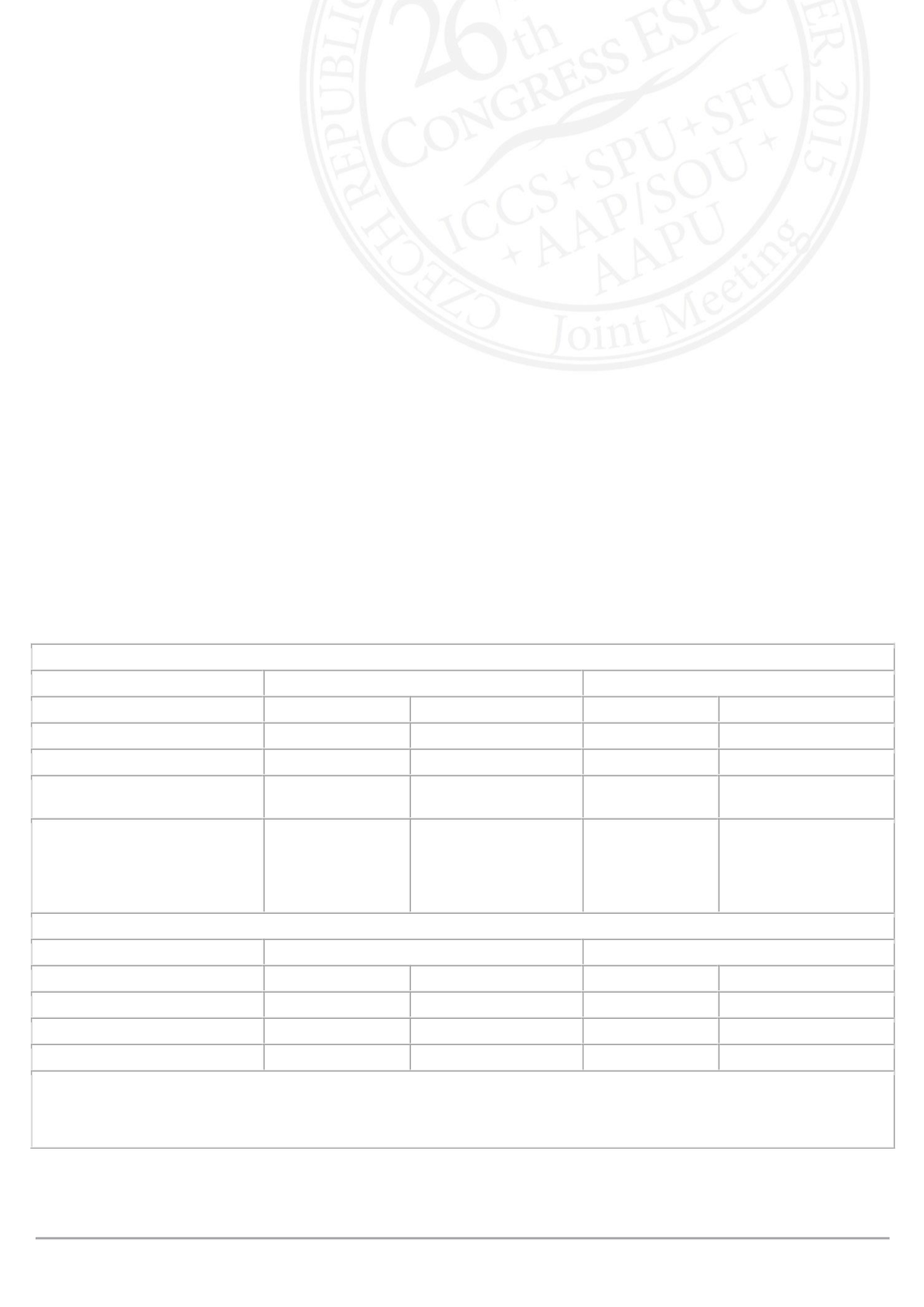
Change from Baseline to End of Treatment in Mean Volume Voided/Micturition (mL) in Children and Adolescents (FAS)
Placebo+standard urotherapy
Solifenacin+standard urotherapy
Children (n=70)
Adolescents (n=19) Children (n=73) Adolescents (n=21)
Baseline Mean (SE)
94.1 (4.6)
169.1 (14.6)
96.9 (4.8)
159.6 (13.4)
End of Treatment Mean (SE)
108.5 (5.4)
185.7 (13.7)
123.1 (6.2)
177.2 (13.4)
Change from Baseline
Adjusted Mean (SE)
13.4 (4.8)
6.9 (14.6)
25.5 (4.8)
2.3 (14.0)
Difference (Solifenacin-
Placebo)
Adjusted Mean (SE)
95% CI
P-value
12.1 (6.0)
(0.2, 24.0)
0.046
–4.7 (15.7)
(–36.7, 27.4)
Incidence of Most Common Drug-Related TEAEs in Children and Adolescents (SAF)†
Placebo+standard urotherapy
Solifenacin+standard urotherapy
Children (n=73)
Adolescents (n=19) Children (n=73) Adolescents (n=22)
Constipation
2.7%
0%
5.5%
0%
ECG QT prolonged‡
2.7%
5.3%
5.5%
4.5%
Dry mouth
1.4%
5.3%
2.7%
0%
CI=confidence interval, ECG=electrocardiogram, FAS=full analysis set, SAF=safety analysis set, SE=standard error,
TEAE=treatment-emergent adverse event
†TEAEs listed represent those with the highest incidence in both age cohorts combined
‡AEs were driven by patients who met the discontinuation criterion in the study
CONCLUSIONS
Solifenacin in a once-daily liquid formulation improved MVV/micturition in children with OAB and appeared safe and well
tolerated.












